Automated real-time, on-line n-glycosylation monitoring methods and systems thereof
At least some embodiments disclosed here may be directed to design and implementation of a novel PAT tool for real-time (or near real-time) online N-glycosylation analysis through the use of sequential injection analysis (SIA) coupled with liquid chromatography; rapid and robust N-glycosylation monitoring during N-glycosylated protein (e.g., monoclonal antibody) bioprocessing enabled by instant, sensitive labeling chemistry; and systems thereof.
This patent application describes an innovative method and system for real-time, automated monitoring of N-glycosylation during the continuous biomanufacturing of biologics, particularly monoclonal antibodies. The invention addresses key challenges in the biopharmaceutical industry’s shift towards continuous manufacturing practices.
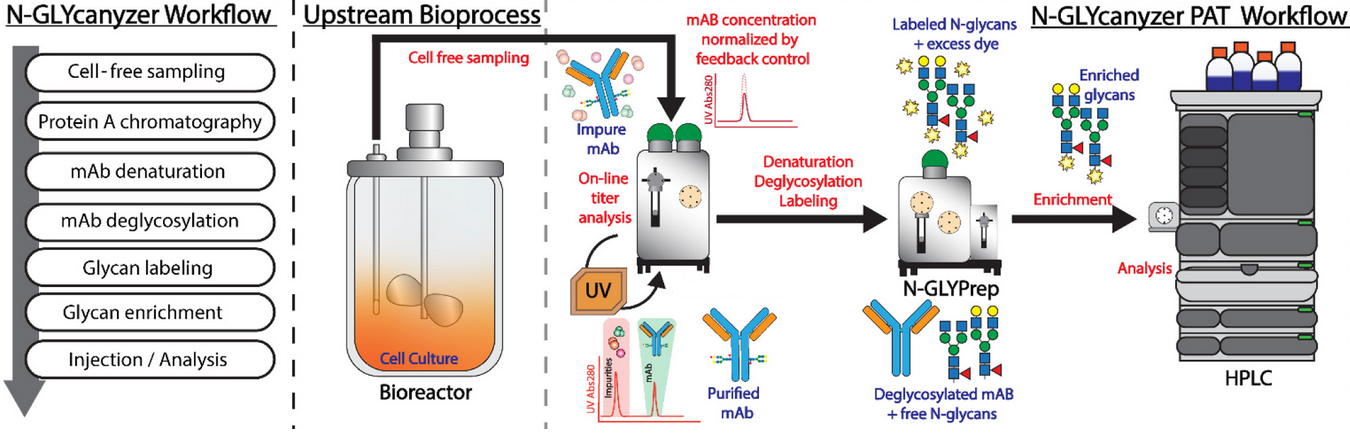
- Real-time or near real-time online N-glycosylation analysis
- Integration of sequential injection analysis (SIA) with liquid chromatography
- Rapid and sensitive labeling chemistry using Instant PC (IPC)
- Automated workflow for continuous sampling, purification, and analysis
- Bioreactor for continuous cell culture
- Protein A column for initial purification
- UV spectrometer for titer and concentration analysis
- Specialized valves and syringe pumps for fluid control
- N-Glycanyzer for glycan analysis
- Continuous sampling from the bioreactor
- Protein purification using a Protein A column
- Denaturation and deglycosylation of the protein
- Rapid glycan labeling using IPC
- Glycan separation and analysis using liquid chromatography
- Effective separation of glycans using liquid chromatography
- Sensitive fluorescent detection (excitation at 285 nm, emission at 345 nm)
- Quantitative analysis through correlation between injection volume and peak heights
- Optimized wash volumes for the trap column
- Capability to analyze small sample volumes (1-16 μL)
This innovation represents a significant advancement in biopharmaceutical manufacturing technology, addressing critical challenges in product quality control, process efficiency, and regulatory compliance. It has the potential to accelerate the development of new biologics and improve the consistency and quality of existing products, shaping the future of biological drug production.